Telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) are becoming increasingly important components of healthcare delivery. However, the use of these technologies has raised concerns about the security and privacy of patient data. As such, it is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure that the patient data collected through telehealth and RPM is secure. In this article, we will discuss the importance of data security in telehealth and RPM, the risks associated with the use of these technologies, and strategies for managing telehealth and RPM data security.
What Is Telehealth?
Telehealth is defined as the delivery of healthcare services using telecommunication technologies, such as videoconferencing, remote patient monitoring, and mobile health apps. It involves the use of technology to provide medical care and services to patients who are not physically present in the same location as the healthcare provider, whether due to long and expensive traveling, physical disabilities, or mental health-related reasons.
Telehealth can be used for a variety of purposes, including consultations with healthcare providers, remote monitoring of chronic conditions, medication management, and mental health services. It is especially useful for patients who live in remote or rural areas, where access to healthcare services may be limited.
There are numerous benefits of telehealth. First, it provides patients with access to healthcare services regardless of their geographic location. This can help to reduce healthcare disparities and improve health outcomes for underserved populations. Second, telehealth can reduce healthcare costs, as it eliminates the need for patients to travel to appointments and can reduce hospital readmissions. Last but not least, telehealth can also improve the patient experience by providing convenient, flexible, and personalized care. Patients can receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes, which can be especially beneficial for patients who have mobility issues or chronic conditions that make it difficult to travel to appointments.
What Is Remote Patient Monitoring?
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) refers to the use of digital devices to measure and monitor patients’ vital signs and health status from the convenience of their own homes. RPM technology allows healthcare providers to monitor their patients at a distance, enabling earlier detection of health issues and providing potential for more timely interventions. Using RPM, patients can track various health metrics, such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels — all of which are crucial to managing a range of chronic conditions. RPM has proven to be highly effective, with studies showing that it can reduce hospital readmissions, improve patient outcomes, and lower healthcare costs. Overall, RPM has the potential to transform the process of healthcare into a more patient-centric, convenient, and efficient system.
Conditions that can be managed via remote patient monitoring include, but are certainly not limited to, the following:
1. Chronic diseases:
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) can help monitor and manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, Obesity, and heart disease. RPM devices can provide real-time data on blood pressure, blood glucose levels, weight, and heart rate, allowing healthcare providers to monitor their patients' conditions remotely and intervene if necessary.
2. Respiratory conditions:
RPM can be used to monitor patients with respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and sleep apnea. Devices can measure breathing rates, oxygen levels, and other vital signs, allowing doctors to track their patient's conditions and make adjustments to treatment plans. In 2022, CMS introduced a new set of CPT codes under Remote Therapeutic Monitoring, an offshoot of RPM, in which these vitals can be monitored and healthcare providers can receive reimbursement.
3. Mental health:
RPM is often used to monitor patients with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Wearable devices can track physical activity, sleep patterns, and other metrics that can provide insight into a patient's mental state.
4. Post-surgical care:
RPM may be used to monitor patients after surgery, allowing doctors to track their recovery remotely and intervene if necessary. Devices can monitor vital signs, wound healing, and other indicators of recovery.
5. Elderly care:
RPM can be used to monitor elderly patients who may have difficulty traveling to medical appointments. Devices can monitor vital signs and other metrics, providing caregivers with real-time data on their patients' health.
6. Pregnancy:
RPM is used to monitor pregnant women, allowing doctors to track fetal heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs remotely. This can help to identify potential complications early on and improve overall pregnancy outcomes.
7. Obesity management:
RPM can also be used to monitor patients with obesity, providing real-time data on weight, physical activity, and other metrics that can inform treatment plans.
8. Rehabilitation:
Remote patient monitoring may be used for patients undergoing physical therapy or rehabilitation. Devices can track movement, strength, and other metrics, allowing therapists to adjust treatment plans and monitor progress remotely.
9. Infectious diseases:
RPM can be used to monitor patients with infectious diseases such as COVID-19. Devices can monitor vital signs and other metrics, providing doctors with real-time data on their patient's health and helping to identify potential complications early on.
10. Chronic pain:
RPM is also used to monitor patients with chronic pain, providing doctors with real-time data on pain levels and other metrics that can inform treatment plans. Devices can also track physical activity and sleep patterns, which can be important factors in managing chronic pain.
Importance Of Data Security In Telehealth and RPM
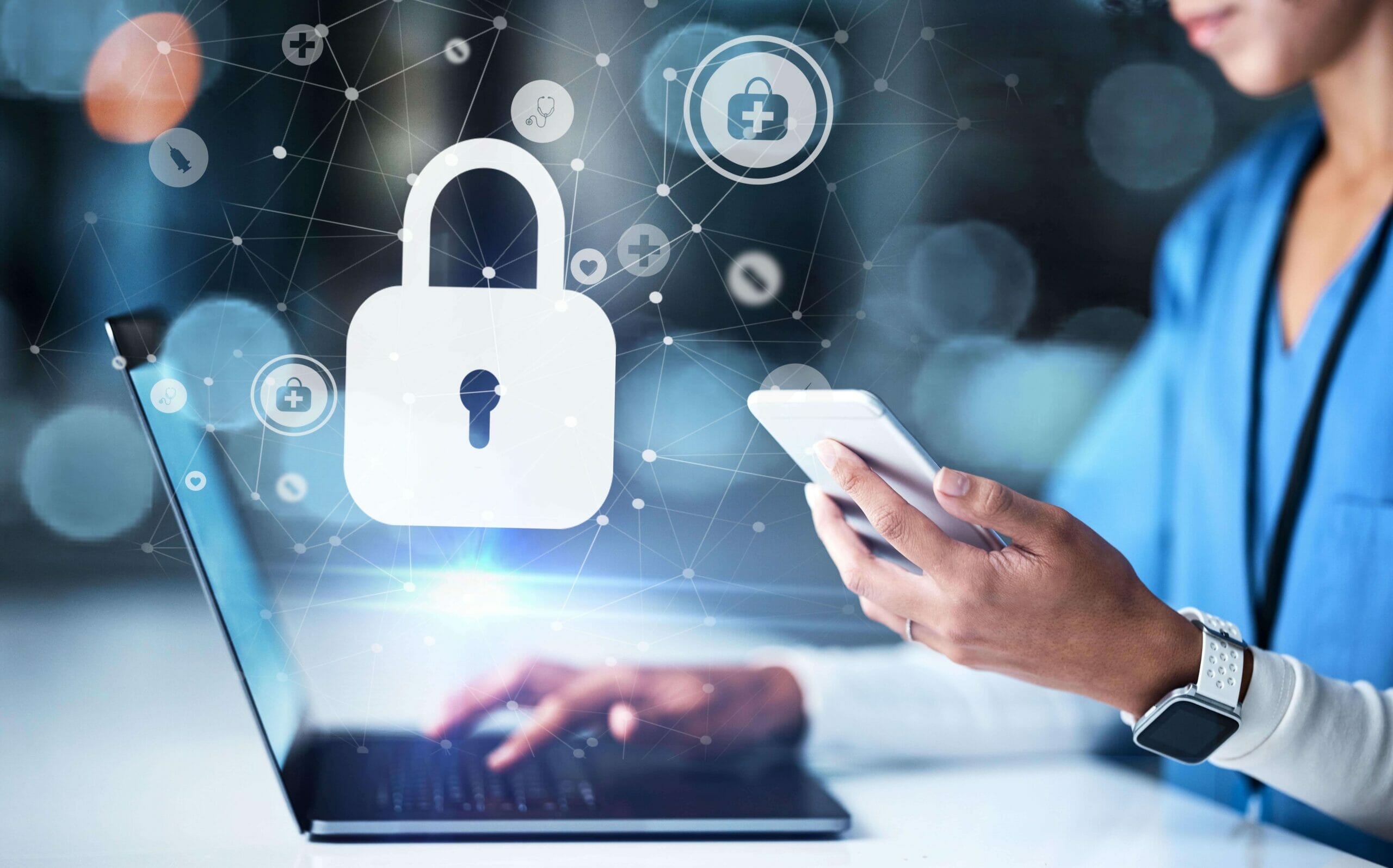
Telehealth and RPM technologies have revolutionized healthcare delivery, allowing healthcare providers to deliver quality care to patients in remote locations, improve patient outcomes, and minimize healthcare costs. However, the use of these technologies has also led to an increase in the volume of patient data collected, stored, and transmitted electronically. This data may include personal health information, such as medical history, medication lists, and diagnostic test results, which must be protected to ensure patient privacy and confidentiality.
Additionally, the use of telehealth and RPM technologies has introduced new cybersecurity risks, including data breaches, identity theft, and ransomware attacks. It is important for healthcare providers to take significant steps to secure patient data in telehealth and RPM systems to avoid these risks.
Risks Associated With Telehealth And RPM
Telehealth and RPM technologies are susceptible to several risks that can compromise the security and privacy of patient data. These risks include:
1. Unauthorized Access:
Unauthorized individuals, including hackers, could try to gain access to patient data in telehealth and RPM systems if proper security measures are not in place. This can lead to the theft of patient data and identity theft.
2. Data Breaches:
Telehealth and RPM systems can be vulnerable to data breaches, which may cause the exposure of patient data. Data breaches may occur because of system vulnerabilities, human error, or malicious attacks.
3. Ransomware:
Ransomware attacks involve the encryption of patient data by hackers, who demand payment to decrypt the data. Ransomware attacks can result in the loss of patient data and can be costly for healthcare providers.
4. Device Security:
Telehealth and RPM systems may be compromised through the devices used to access them, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. These devices may be lost or stolen, leading to the loss of patient data.
To Learn More, Download Our White Paper: The Importance of Health Data Security Workflows in Remote Patient Monitoring and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring
The Benefit Of A Private RPM Network
Smart Meter offers the only private RPM data network. This ensures that data transmission is secure and protected from outside interference, as only authorized devices are granted access. A private RPM data network also reduces the risk of data breaches, which can compromise sensitive information and lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Additionally, a private RPM data network can improve the efficiency and reliability of communication, as it can be customized and optimized to meet specific needs. Finally, a private RPM data network allows you to have greater control over your data, as you are not dependent on third-party providers for communication services.
Other benefits include:
- Increased accuracy of data readings
- More efficient use of healthcare resources by reducing in-person visits and unnecessary hospitalizations
- Greater flexibility and convenience for patients to manage their health from the comfort of their own homes
- Better access to care for people living in remote or underserved areas who may have limited access to in-person healthcare services
- Enhanced data security and privacy protection for sensitive health information
- Improved communication and real-time data sharing between individuals and their healthcare providers
Managing Telehealth and RPM Data Security
To manage the risks associated with telehealth and RPM, healthcare providers must implement effective data security measures. These measures should include the following:
-
Data Encryption:
Telehealth and RPM data should be encrypted to protect them from unauthorized access. Encryption involves converting data into a code that can only be deciphered by authorized individuals.
-
Access Controls:
Healthcare providers should implement access controls to restrict access to patient data to authorized personnel. Access controls should include strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access.
-
Data Backup:
Telehealth and RPM data should be regularly backed up to prevent the loss of patient data in the event of a data breach or ransomware attack.
-
Device Management:
Healthcare providers should implement device management policies to secure the devices used to access telehealth and RPM systems. This may include the use of mobile device management software to remotely wipe data from lost or stolen devices.
-
Training and Awareness:
Healthcare providers should provide training to employees on telehealth and RPM data security to ensure they are aware of the risks associated with these technologies and understand how to use them securely.
-
Compliance:
Healthcare providers must comply with relevant laws and regulations governing the collection, storage, and transmission of patient data. This includes the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States.
Why Choose Smart Meter?
Smart Meter offers the only private RPM data network. Our innovative RPM devices allow for continuous monitoring of vital signs, blood glucose levels, and other important health metrics, providing patients and healthcare providers with valuable data and insights. Let us help you take control of your health and receive the care you need, wherever you are.
Contact us today to learn more.